LATEST NEWS
Press releases & Product news
Cutting small metallographic specimens: tips for going from tricky to easy
2025-06-19
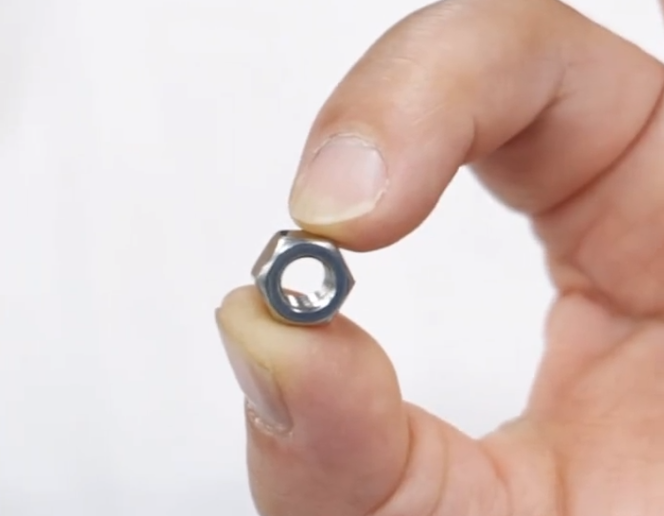

In the process of metallographic sample preparation, cutting of small-sized metallographic samples has always been a headache. The reason why cutting of small-sized metallographic samples is difficult is mainly due to the following pain points.
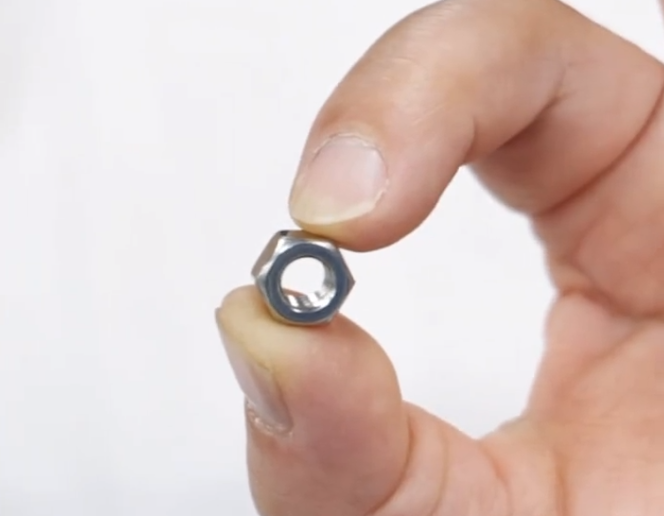

First, the sample is small in size, and conventional fixtures cannot provide sufficient clamping force, cannot be stably fixed, and are very easy to shift during cutting.
Secondly, the heat dissipation area of small samples is small, and the heat generated during the cutting process is difficult to dissipate quickly. Local heat accumulates rapidly, which can easily lead to material phase change and tissue burns, seriously affecting subsequent inspection and analysis.
Furthermore, small samples require extremely high cutting positioning accuracy. Ordinary equipment is difficult to accurately align the cutting line, and a slight deviation may lead to cutting errors.
In addition, after cutting, small samples are prone to falling and rushing into the lower water tank. Once lost, all previous efforts will be wasted.
In addition, the choice of cutting disc is also crucial. If the thickness is not appropriate, the material removal rate will be too high when cutting small samples, and the key areas that need to be inspected and analyzed will be damaged.
However, don't worry! In response to these problems that have plagued the industry for a long time, we have summarized a set of effective solutions to help you easily overcome the difficulties in cutting small-sized metallographic samples.
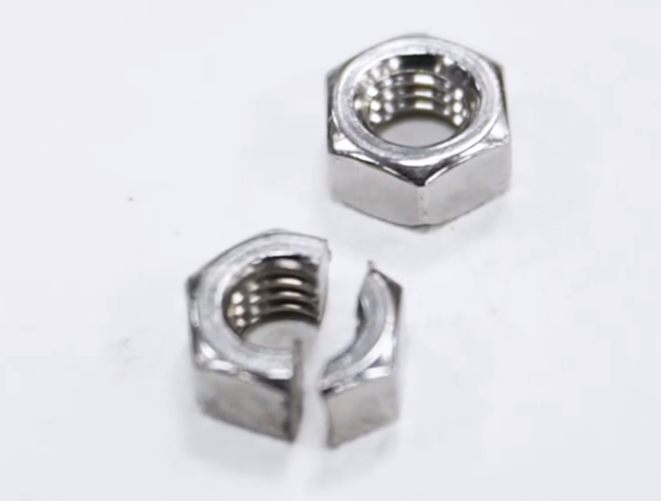

1. Precision fixture, rock-solid
The key to solving the difficulty of clamping small specimens is to use precision fixtures. This type of fixture is specially designed to provide accurate and stable clamping force, firmly fix small-sized specimens, and prevent displacement and splashing.
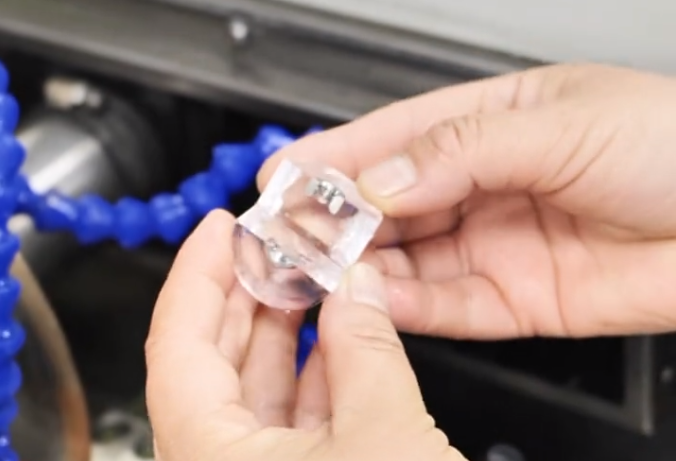
2. Mounting assistance, making things easier
Mounting assistance is a clever way to handle small specimens. Mounting small specimens in resin to make them regular, larger-volume specimens. This not only makes it easier to clamp, but also effectively protects the edges of the specimens. After cutting, you can either grind the mounting specimens directly, or carefully break the cut mounting specimens, take out the specimens and re-mounting them, so as to flexibly respond to different testing needs.

3. Precision cutting, precise temperature control
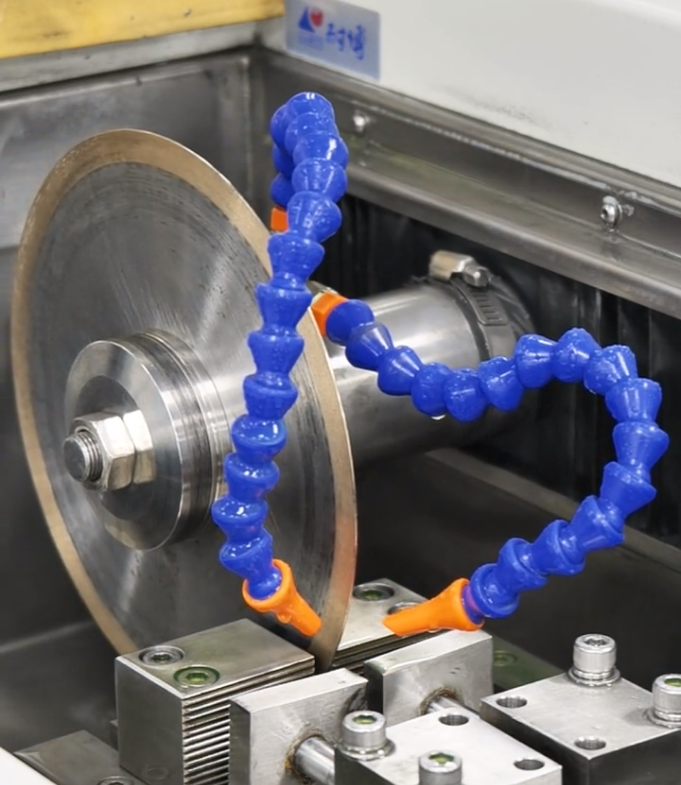
The metallographic precision cutting machine produced by LABTT is a powerful assistant for cutting small samples. It has the characteristics of low speed and high-precision feeding, and can accurately control the cutting process to ensure that the cutting line perfectly matches the target area. When used with LABTT's own consumable ultra-thin diamond cutting blade, it can greatly reduce material loss and thermal damage, and retain the original tissue state of the sample to the greatest extent.
At the same time, the continuous small flow spray cooling method directly aimed at the cutting area can not only effectively remove the heat generated by cutting, but also avoid the displacement of the sample caused by liquid flow impact.
4. Thoughtful design to prevent loss
To prevent small samples from falling and being lost after cutting, you can choose equipment with a sample collection net. This small design can play a big role. When the sample is cut, the sample collection net will catch the sample in time to prevent it from falling into the water tank.
Although it is difficult to cut small-sized metallographic samples, as long as you master the correct methods and tools, you can solve the problems one by one. Follow us to share more practical tips for metallographic sample preparation!


